
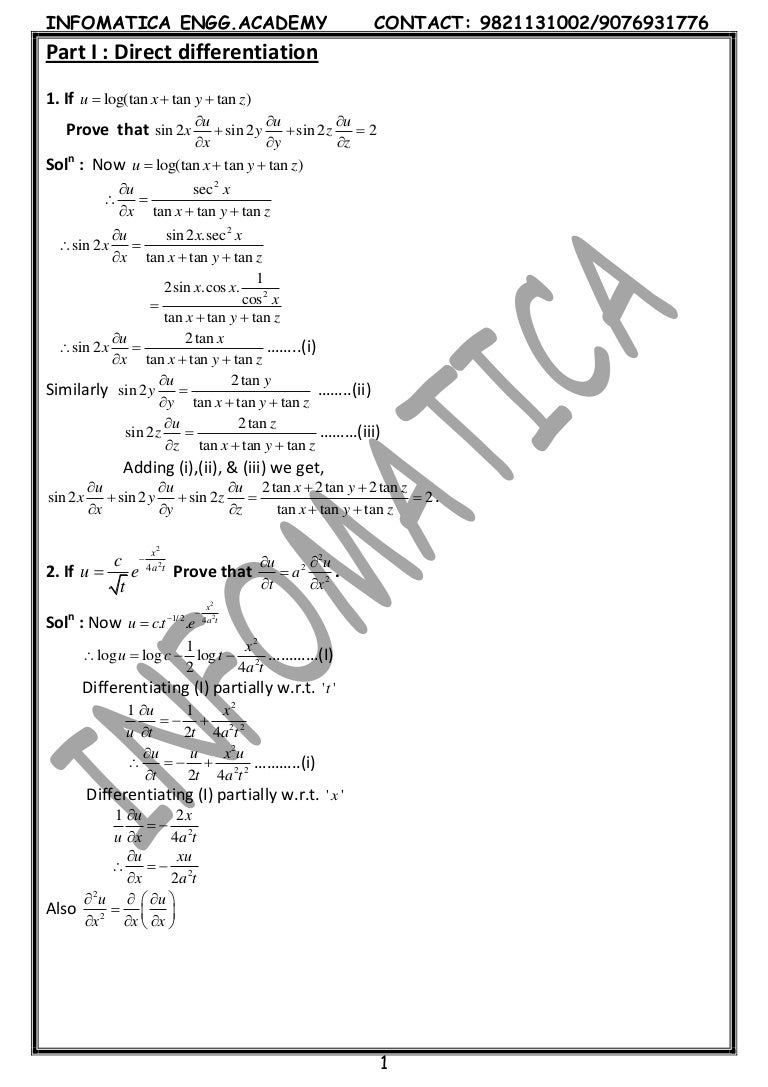
Find The Second Order Partial Derivatives Of The Given Itprospt
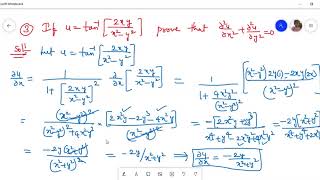
Here z is a homogeneous function of the form x n f (y/x) Here n = 2 So by Euler's theorem x∂z/∂x y ∂z/∂y = nz (ii) ∂z/∂x = sec 2 u ∂u/∂x (from (i)) ∂z/∂y = sec 2 u ∂u/∂y Substitute above 2The quadratic formula gives two solutions, one when ± is addition and one when it is subtraction x^ {2}2yxy^ {2}=0 x 2 2 y x y 2 = 0 This equation is in standard form ax^ {2}bxc=0
Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is
Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is-But avoid Asking for help,Enter your 10 digit mobile number to receive an OTP 91 Submit

Ex 5 3 10 Find Dy Dx In Y Tan 1 3x X3 1 3x2 Ex 5 3
1y2 = √ 1 sinxdx =⇒ tan−1y = −2 √ 1− sinxC y(0) = 1 =⇒ C = π 4 2 Therefore y(x) = tan(π 4 2(1− √ 1−sinx)) 3 Interval of definition By looking at an initial value problem dy/dx = f(x,y)Consider the curve given by y^2 = 2xy (a) show that dy/dx= y/(2yx) (b) Find all points (x,y) on the curve where the line tangent to the curve has slope 1/2 (c) Show that there are now points (x,y) Answer Correct option is A (2cos2u−1)sin2u Given u=tan −1 ( x−y x 3 y 3) tanu= x−y x 3 y 3 (x−y)tanu=x 3 y 3 →(1) Differentiate wrt ′ x
Explanation We will be differentiating implicitly On the left hand side, we will use the chain rule in regards to the inverse tangent function d dx (arctan(u)) = u' 1 u2 Also, note thatFind dy/dx by implicit differentiation x^3 3x^2y 2xy^2 =12 Please show me the work/steps on how to do it math For the curve given by 4x^2y^2=4xy, show that there is a point P with xClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If u = x^2tan^1(y/x) y^2tan^1(x/y) , then find ∂^2u∂x∂y Solve Study Textbooks Guides Join / Login
Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) isのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
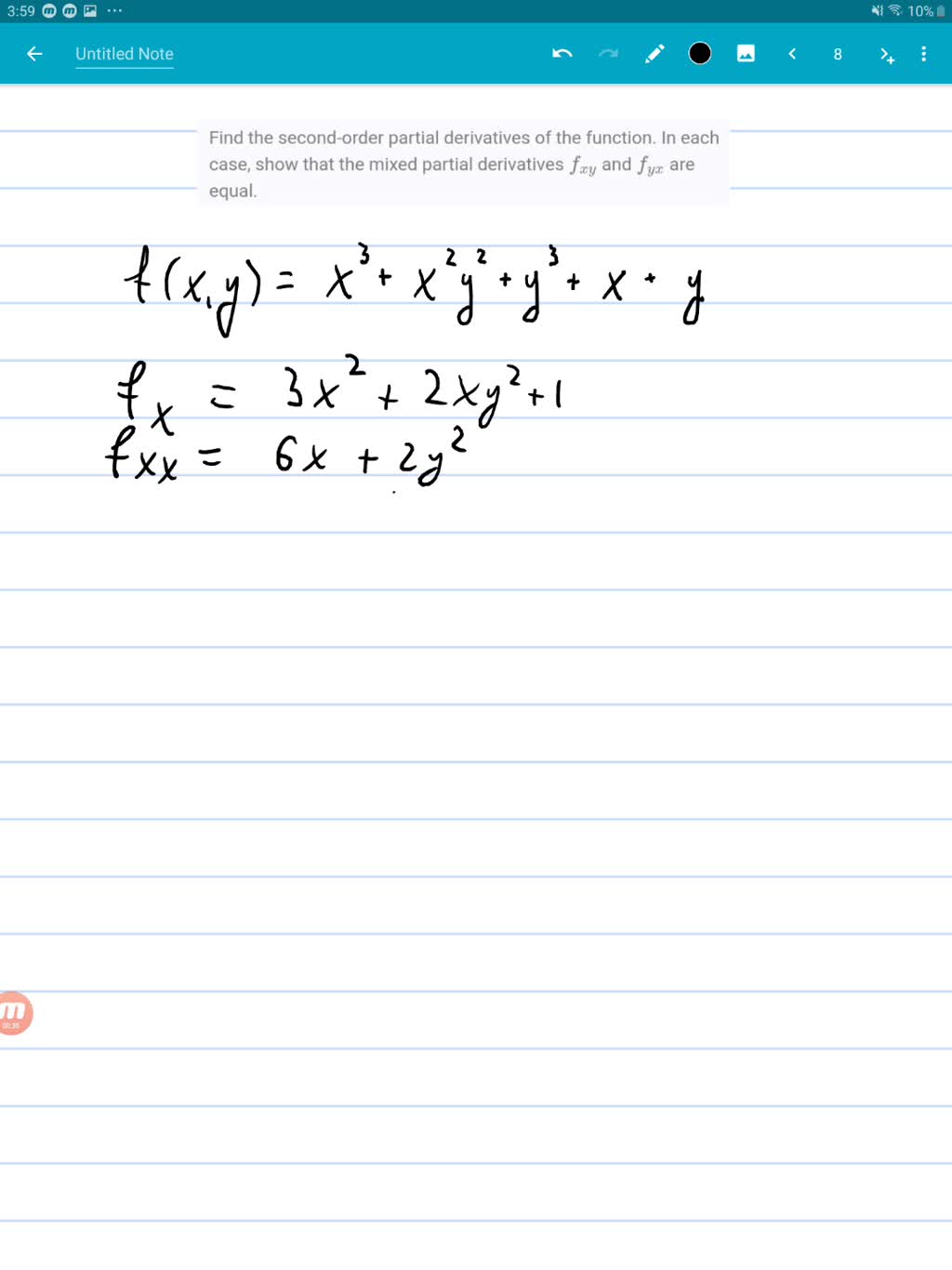 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
 | 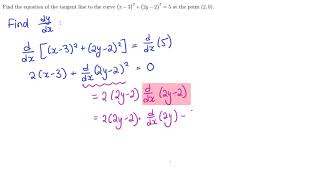 | |
「Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
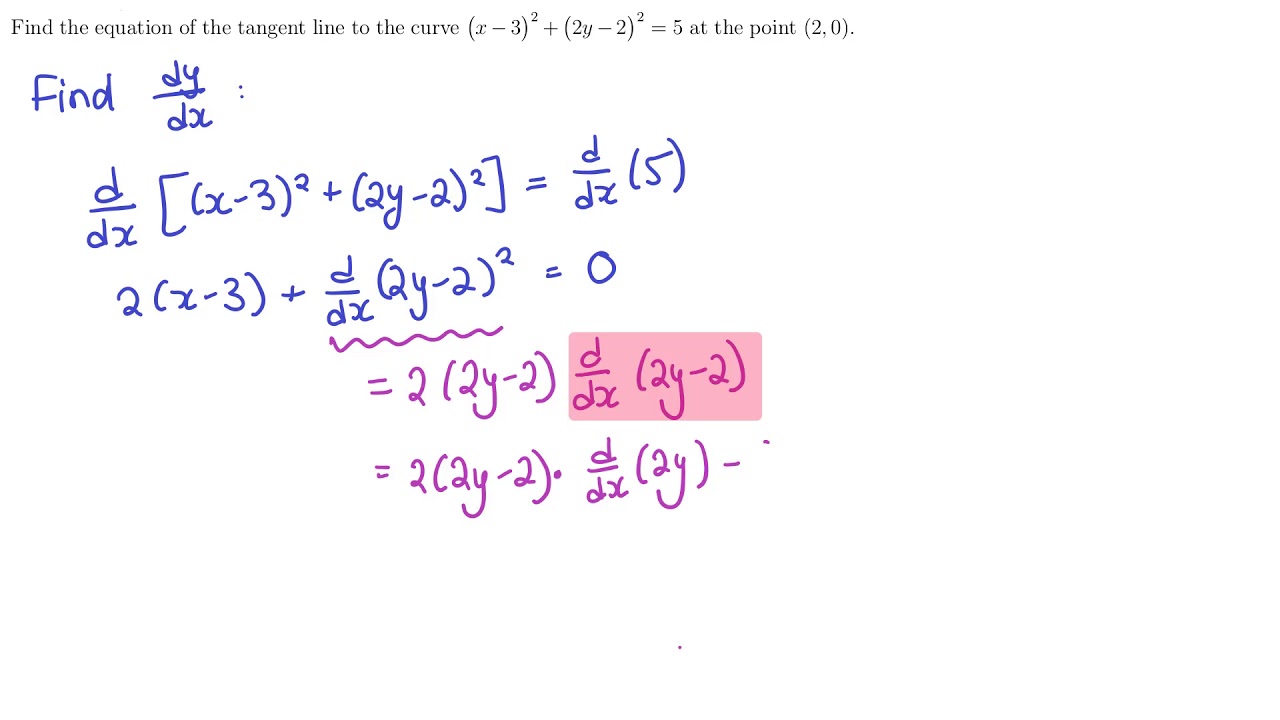 |  | |
「Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | 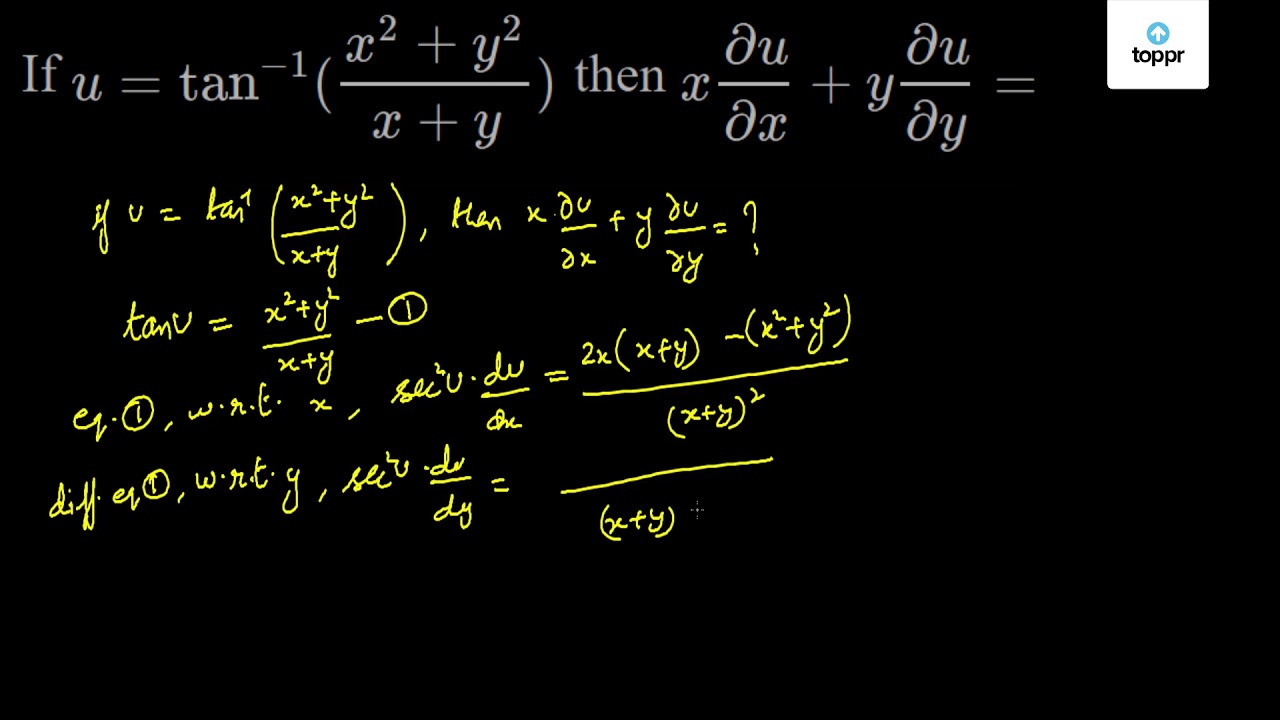 |
 |  | |
「Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 | ||
 |  | |
「Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
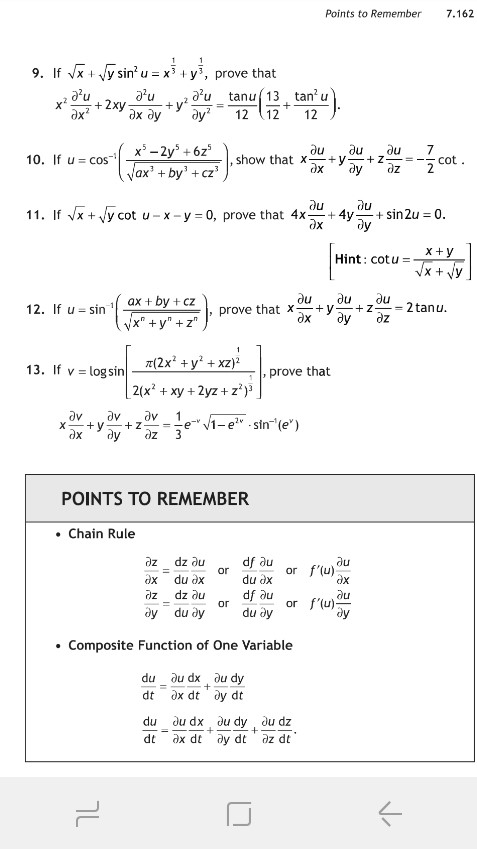
Download PDF's Class 12 Class 11 Class 10 Class 9 Class 8 Class 7 Class 6 NCERT Easy Reading Alleen Test Solutions Blog About Us Career Bs GREWAL EXERCISE SOLUTION 192 A number of the form xiy, where x and y are real numbers and i= (1) ^ SOLVE THE EQUATION 6X^311X^23X2=0 Given roots are in HP
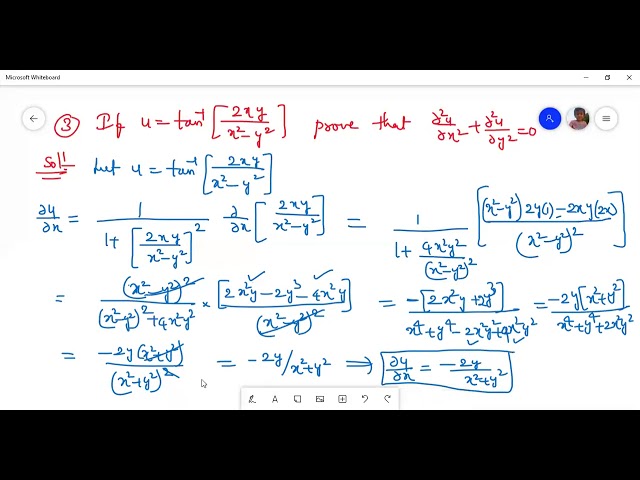
Incoming Term: u=tan^-1(2xy/x^2-y^2), y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is, if y=tan^(-1)x then (1+x^(2))y_(2)+y_(1) is, y=tan^(-1)x prove that (1+x^(2))y(2)+2xy(1)=0, y=tan^(-1)x show that (1+x^(2))y_(2)+2xy(1)=0,



